Accelerating Individualisation is a megatrend changing societies around the world. This megatrend stems from powerful, interconnected social and technological developments.
Customisation, and a proliferation of options for consumers, has replaced mass production and a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach, which characterised business in the post-war era.
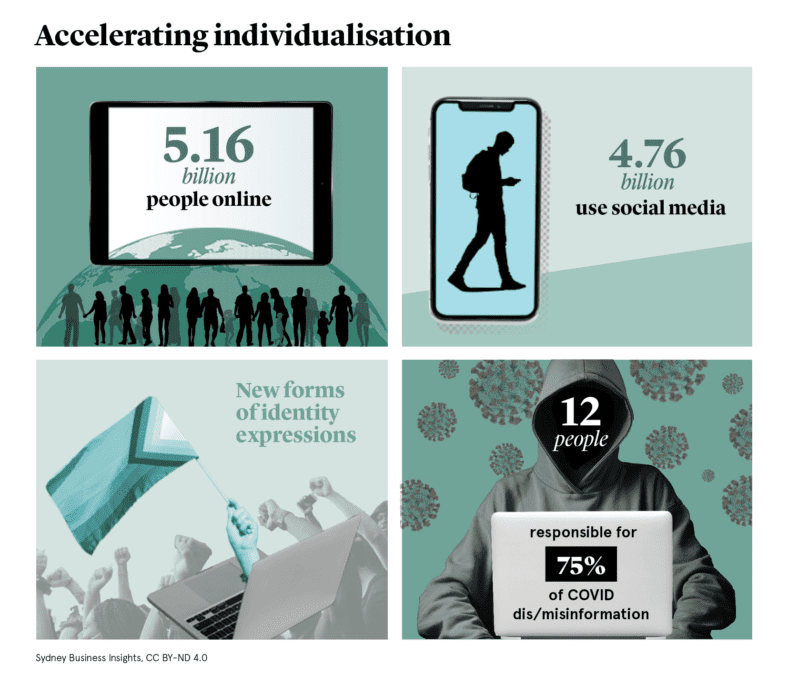
One important factor driving this customisation is the availability of a staggering amount of data. This has been made possible due to changes in technology. The widespread use of smartphones and access to the internet have provided unparalleled information about our preferences. Our ‘digital footprint’ informs business decisions and shapes offerings for customers, resulting in hyper-personalised products and services.
Social media and other digital forums, used by 4.76 billion people worldwide, have enabled many new online communities. It is easier than ever for superfans, gardeners, gamers, squash players, and conspiracy theorists to meet others with similar interests from around the world. Algorithms have also created echo chambers, amplifying political polarisation in many countries.
Social media also places the focus on the self, and encourages selective self-presentation. These platforms enable individuals to influence others and effect change – from activists and populist leaders, through to Instagram influencers and TikTok celebrities.
These platforms also facilitate the spread of misinformation and disinformation, distorting personal and public conversations, with serious implications for social cohesion and public well-being. Social media is also blamed for the rise in anxiety, depression and self-harm, particularly in people born since the turn of the century. Experts have expressed concern about how this increased fragility will affect individuals’ work lives, and its impact on creativity and innovation.
The way we work is also changing. In many industries, instead of being in the office from 9 to 5, people are now part of a flexible, more distributed and individualised workforce. Especially since COVID-19, technology has enabled remote and hybrid work, accelerating freelancing and the gig economy.
New forms of identity expression are also flourishing. Intersecting differences in sex and gender, age, ethnicity, subcultures and beliefs are also reflected in business, with the marketplace increasingly catering for diverse communities.
Accelerating Individualisation has many points of connection to the technology megatrend. Both will increase in impact as this century progresses.
Ritchie, H., Mathieu, Roser, M., Ortiz-Ospina, E. (2023). ‘Internet’, Our World in Data. Available at: https://ourworldindata.org/internet
Petrosyan, A. (2023). ‘Worldwide Digital Population 2023’, Statista. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/617136/digital-population-worldwide/
Kemp, S. (2023). Digital 2023: Global Overview Report, Data Reportal. Available at: https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2023-global-overview-report
Varadarajan, T. (2022). ‘Jonathan Haidt on the ‘National Crisis’ of Gen Z’, Wall Street Journal 30/12/22. Available at: https://www.wsj.com/articles/the-national-crisis-of-generation-z-jonathan-haidt-social-media-performance-anxiety-fragility-gap-childhood-11672401345
Salam, E. (2021). ‘Majority of Covid misinformation came from 12 people, report finds’, The Guardian 18/7/21. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/jul/17/covid-misinformation-conspiracy-theories-ccdh-report
We believe in open and honest access to knowledge. We use a Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivatives licence for our articles and podcasts, so you can republish them for free, online or in print.